Navigating Medicaid Expansion – Alabama Following Arkansas Approach
Unpacking the States’ Models for Broadening Medicaid Coverage

THE VBP Blog
June 8, 2023 – Medicaid expansion remains a pivotal issue within the United States, underscoring the broader debate around equitable healthcare access. While Medicaid expansion is optional for states, as of March 2023, 41 states, including Washington DC, have expanded Medicaid.
In addition to these 41 states, Alabama is currently contemplating Medicaid expansion. Within this complex narrative the state is considering following the unique approach that Arkansas has taken to Medicaid expansion. In this blog, we are going to into the nuances of Medicaid expansion in these two states. Keep reading to learn more about their distinct strategies, the potential impact of these models, and future expectations.
What is Medicaid Expansion and Why Does it Matter?
Medicaid expansion is a critical lever in the healthcare system. It directly targets the ‘coverage gap’ in insurance. This gap consists of low-income adults who earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but too little to be eligible for the Affordable Care Act’s (ACA) premium tax credits. This leaves many individuals without viable options for affordable health coverage and thus, many go without the care they need. Through Medicaid expansion, states can extend coverage to these individuals and help ensure that more people have access to affordable healthcare.
There are many benefits of Medicaid expansion. Per a report from the Kaiser Family Foundation, Medicaid expansion could extend eligibility to millions of uninsured adults. Not only does this provide them with essential health coverage, but it also alleviates the financial burden often associated with out-of-pocket healthcare costs. With health coverage, these individuals are also more likely to receive preventative care, which can lead to better overall health outcomes.
But the benefits of Medicaid expansion aren’t limited to the individuals that receive coverage. Healthcare providers, particularly those in underserved or rural areas, also benefit from Medicaid expansion. By reducing the number of uninsured patients, Medicaid expansion can help lower the level of uncompensated care that hospitals must provide. This improves their financial stability and allows them to invest more in attracting and retaining providers.
Medicaid expansion can have broader socioeconomic benefits. It can stimulate the economy by bringing in federal dollars, creating jobs in the health care sector, and reducing state spending on programs for the uninsured. All these factors make Medicaid expansion not just a health policy issue, but a significant component of the broader economic and social wellbeing of a state. These benefits are also why over 80% of states have adopted Medicaid expansion in some form or fashion. Alabama may be next to do so, but only time will tell.
The Current State of Medicaid Expansion in Alabama
Despite the initial reluctance, Alabama’s lawmakers are now considering Medicaid expansion as a necessary step towards improving the health of their residents. The Alabama House Health Committee recently held an educational meeting on addressing the state’s coverage gap. The meeting featured presentations from the Alabama Hospital Association and Blue Cross Blue Shield of Alabama. Both stated their support for expanding Medicaid and the social and economic benefits of providing insurance to Alabamians without through Medicaid expansion.
Healthcare facilities in the state, especially hospitals, have been instrumental in propelling this change of heart. Their argument hinges on the twin benefits of economic growth and improved health outcomes that such expansion would entail.
Medicaid expansion is expected to bridge the coverage gap for approximately 300,000 Alabamians. These are the individuals in the state who currently do not qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance either. This expansion is not only about providing insurance cards to these individuals. It also carries significant implications for broader public health and would ensure better health outcomes and reduce healthcare disparities among the population.
The economic impact of the proposed expansion is also considerable. Medicaid expansion could inject over a billion dollars into Alabama’s economy and would create jobs as well. All of this would invariably stimulate the local economy.
This economic jolt could also help to avert the closure of hospitals. According to Danne Howard, deputy director of the Alabama Hospital Association, hospitals in the state provide about $600 million in uncompensated care. Since hospitals must absorb the costs when medical bills do not get paid, Medicaid expansion can help hospitals stay open, especially in rural Alabama, which ensures the continued availability of healthcare services in those areas.
While the state is looking for an “Alabama-driven solution,” they are also considering the approaches of other states. Primarily, they are looking at Arkansas’ Medicaid expansion model.
Arkansas's Innovative Medicaid Expansion – The Private Option
Arkansas has taken an innovative approach to Medicaid expansion by adopting what is known as ‘the private option.’ Under this model, the state uses Medicaid funds to purchase private insurance for eligible beneficiaries. The benefit of this approach is that it enables those who would otherwise qualify for Medicaid to access the same set of services and providers that are available to individuals with private insurance.
Through the private option model, Arkansas provides health insurance to people living under the 138% Federal Poverty Level by enrolling most qualifying residents in a private health plan. Those who have complex medical needs or those with disabilities who need more medical care are generally enrolled into traditional Medicare. This helps keep plans in the private option more affordable, and thus far Arkansas has been able to provide health insurance to the state’s working population while keeping costs at or below what the federal government requires.
While other states have tried the private option model, many have failed to sustain success. Both New Hampshire and Iowa started with a private option approach, but both have since transitioned to Medicaid managed care to reduce costs and improve coordination of care.
Arkansas on the other hand, has observed a dramatic reduction in the percentage of its uninsured population. The shift marks one of the largest reductions in the percentage of uninsured residents in the nation. The program has also seen lower Medicaid spending per enrollee for adult beneficiaries under the Medicaid expansion.
The model has led to a significant decline in uncompensated care costs for hospitals, thus relieving them of a substantial financial burden. According to Dr. Joe Thompson, president & CEO at Arkansas Center for Health Improvement (ACHI), before Medicaid expansion, about 16% of their patients had no source of payments. After expansion that dropped down to 4%. This is especially important in rural areas where healthcare providers are already reeling from physician attraction and retention and struggling to keep their doors open. By reducing uncompensated care, access to healthcare can be expanded.
While there have been benefits of the private option, it is not without its critics. Some argue that it functions as a vehicle for transferring government subsidies to insurance companies. Others point to the potentially higher administrative costs associated with this model, compared to traditional Medicaid. In response to these criticisms, Arkansas launched Arkansas Works, now known as Arkansas Health and Opportunity for Me program, or ARHOME. This is a program that incorporates features such as premium assistance, health savings accounts, and encourages individuals to be an active partner in their health outcomes.
The state is also contemplating adding a work requirement for able-bodied adults who receive enhanced Medicaid coverage under the Medicaid expansion program, which is something to keep an eye on.
Moving Forward – What Can We Expect in Alabama?
Alabama finds itself at a pivotal moment. As the map below shows, Alabama is part of a cluster of states in the South that have resisted Medicaid expansion. But as talks pick up regarding finally adopting Medicaid expansion in line with the majority of the country, the fate of health coverage for over 300,000 Alabamians hangs in the balance. The potential benefits of Medicaid expansion are indeed considerable – from improving health outcomes to stimulating the economy, but will talks continue advancing? That remains to be seen. Despite strong support for expansion, there are currently no bills under active consideration.
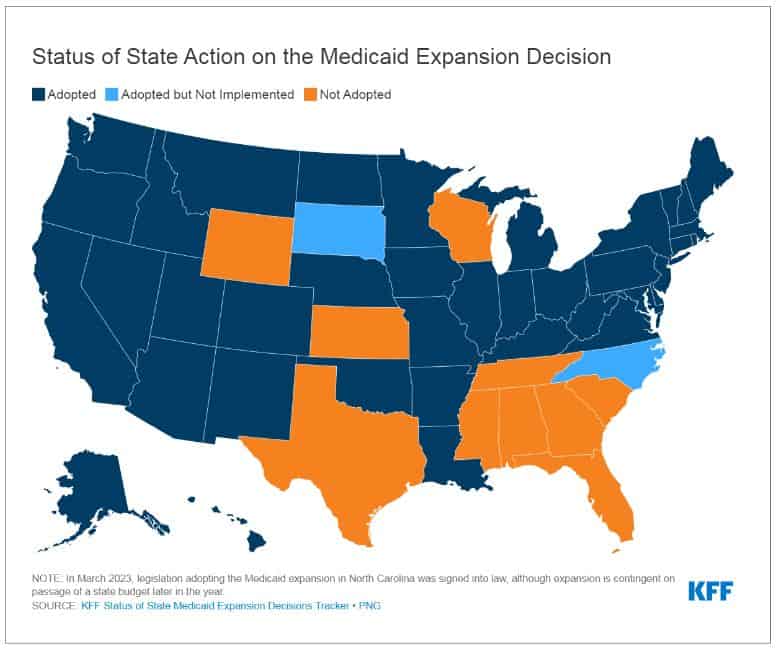
If Alabama does move forward with Medicaid expansion, it will be critical to monitor the developments of other states, such as Arkansas, and draw lessons from their model. However, the state must also adopt strategies based on the unique needs and circumstances of Alabama. The ultimate goal of Medicaid expansion must remain clear – to extend comprehensive and affordable healthcare to all and thus improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare disparities.
Advocates Perspective
One of the crucial aspects that Alabama might want to consider is how to achieve the delicate balance between ensuring comprehensive coverage and managing costs effectively. This balancing act is especially important given that Alabama plans to fund its expansion primarily through an increase in tobacco tax and a public-private partnership. Ultimately, the success of any approach to Medicaid expansion will depend on how well it can balance the dual objectives of improving health outcomes and ensuring financial sustainability. As we watch these developments unfold, it’s clear that the path to Medicaid expansion remains a challenging yet necessary journey towards achieving health equity. Looking ahead, we will likely see more states grappling with these issues and exploring innovative solutions for Medicaid expansion. Regardless of the specific models they adopt, the focus should remain on promoting health equity, ensuring access to quality care, and improving the health outcomes of their residents.
Onward!
Share This Blog!
Get even more insights on Linkedin & Twitter

About the Author
Fady Sahhar brings over 30 years of senior management experience working with major multinational companies including Sara Lee, Mobil Oil, Tenneco Packaging, Pactiv, Progressive Insurance, Transitions Optical, PPG Industries and Essilor (France).
His corporate responsibilities included new product development, strategic planning, marketing management, and global sales. He has developed a number of global communications networks, launched products in over 45 countries, and managed a number of branded patented products.

About the Co-Author
Mandy Sahhar provides experience in digital marketing, event management, and business development. Her background has allowed her to get in on the ground floor of marketing efforts including website design, content marketing, and trade show planning. Through her modern approach, she focuses on bringing businesses into the new digital age of marketing through unique approaches and focused content creation. With a passion for communications, she can bring a fresh perspective to an ever-changing industry. Mandy has an MBA with a marketing concentration from Canisius College.